One of the biggest modern manufacturing challenges is understanding the functioning and operations of different processes. Proper knowledge of the differences between CNC milling and CNC turning will help you choose the right process for the best results.
These are custom machining processes that contribute to subtractive machining. CNC milling and turning processes sometimes overlap. They are both suitable for small and large components and different raw materials. However, they use fundamentally different methods for removing materials.
The differences in their operations make them ideal for specific applications. Therefore, this article will take you through the basics of CNC turning and CNC milling. You will also learn the various differences between these CNC machining processes. Let’s get right to it!
What is CNC Milling?
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling is a common manufacturing process. Manufacturers employ this process in producing a wide range of machined parts. It is also a suitable technique for prototyping companies for making one-off functional prototypes.
CNC milling works by using computer instructions to rotate cutting tools rapidly along 3 or more axes. The machine rotates a cutting tool all over the surface of a stationed or non-mobile workpiece. The spindle grips the milling cutter that rotates at high speed to cut all unwanted material off the surface of the workpiece.
When the CNC milling cutting tool contacts the workpiece, the material is removed in a controlled manner. Workpieces with flat and irregular surfaces on rectangular or square blocks are perfect for the milling method. The tool passes successively against the workpiece’s surface until it resembles the intended end product. CNC mills often keep workpieces stationary, using a vice to hold them on the machine bed.
However, multi-axis mills may rotate workpieces to achieve greater cutting angles. As a result, you can create more complex machined parts without manual reorientation. A CNC milling cutter comes with 2 to 150 cutting surfaces depending on the requirements. There are different types of milling cutters. The common ones are:
- face milling cutters
- hollow milling cutters
- side milling cutters
- end milling cutters
- plain milling cutters
This process was devised as a better replacement for manual machining processes due to its reliability and precision in machining final products. Machinists who handle projects with complex shapes find the milling process very helpful because it is time-saving.
Specialties of CNC Milling
There are several reasons why manufacturers choose CNC milling for machining CNC parts. These include:
Increased Production Capability
CNC milling fits perfectly for businesses that manufacture small batches of parts in a single operation. The CNC milling machine is also compatible with thermal, electrical, mechanical, and chemical processes. Therefore, there is the capability to produce a wide range of components for several industries.
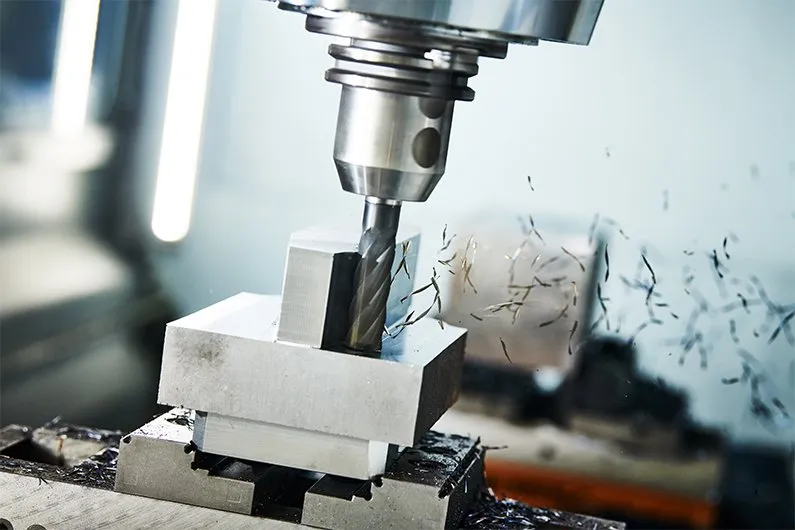

Efficient Use of Material
CNC milling helps manufacturers to reduce materials used in a milling operation. CNC milling has a low material consumption level when compared to CNC turning. As a result, manufacturers enjoy the reduced material costs in huge projects. The CNC milling process also helps you effectively manage material wastes.
Cutting Tools
Working with a CNC mill does not require plain or direct tooling. You can use different cutters (cutting tools) or more than one tool for various operations. In this case, milling is a better and more efficient option than lathes.
CNC mills often facilitate the processing of complex-shaped parts. On the other hand, the lathes used in CNC turning may limit operational capabilities.
Product Specification
CNC milling boasts of its ability to work on a wide range of parts. It can handle complex-shaped parts in the same way it handles simple parts. This renders the CNC mill an ideal option for several projects.

What is CNC Turning?
This metal fabrication process is widely used for creating cylindrical, conical, and rounded parts. It is a popular CNC machining and rapid prototyping processes. However, it is not as versatile as CNC milling.

CNC turning uses machines known as CNC lathes machines or CNC turning centers. These machines consist of a gripping tool known as a chuck and a rotating spindle. The working of the machines differs from CNC mills because they rotate the workpiece rapidly in the chuck. However, the cutting tool does not rotate.
The cutting tool is fixed to the turret, and it moves towards the rotating workpiece to remove materials where necessary. A CNC turning machine can cut the workpiece’s outside. It can also bore through the interior, creating tubular components. The turret may also have multiple cutting tools, and each tool can be engaged individually.
You should note that the machine, the raw material type involved, and the part’s features may affect the machining results. CNC turning machines works well just as the CNC milling machines, although it is considered second best to CNC milling.
Turned workpieces are often smaller in size than milled workpieces. As a result, the CNC turning process works faster and more effectively than the milling method. The mode of operation of the CNC lathe machines and CNC turning centers prevent them from working on parts that need highly accurate detailing.
Specialties of CNC Turning
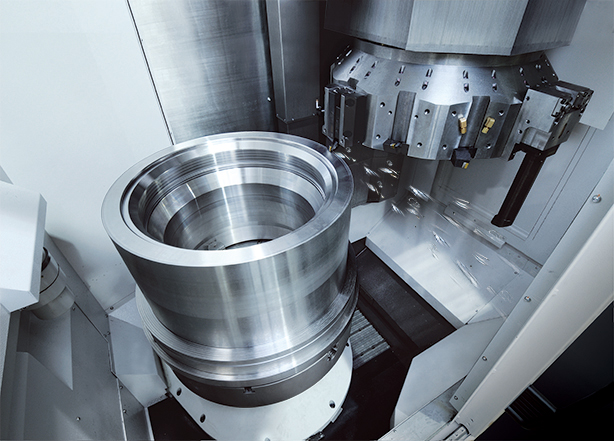

Adaptability
CNC turning is adaptable to several situations as it fits perfectly with other methods to get the desired results. CNC turning can also work with CNC milling based on certain industrial requirements of some parts. It can produce small machine components such as bolts and nuts as well as larger components like turbines.

CNC Machining Accuracy
CNC turning has excellent precision and can complete the desired surface finish operations. Therefore, manufacturers prefer it for essential cylindrical parts or curved surfaces such as rollers, gears, bullets, and drilling bits.
High Production Speed
CNC turning also works faster on workpieces when boring, drilling, or shaping. This helps machinists keep up with deadlines on projects while increasing production capacity simultaneously.
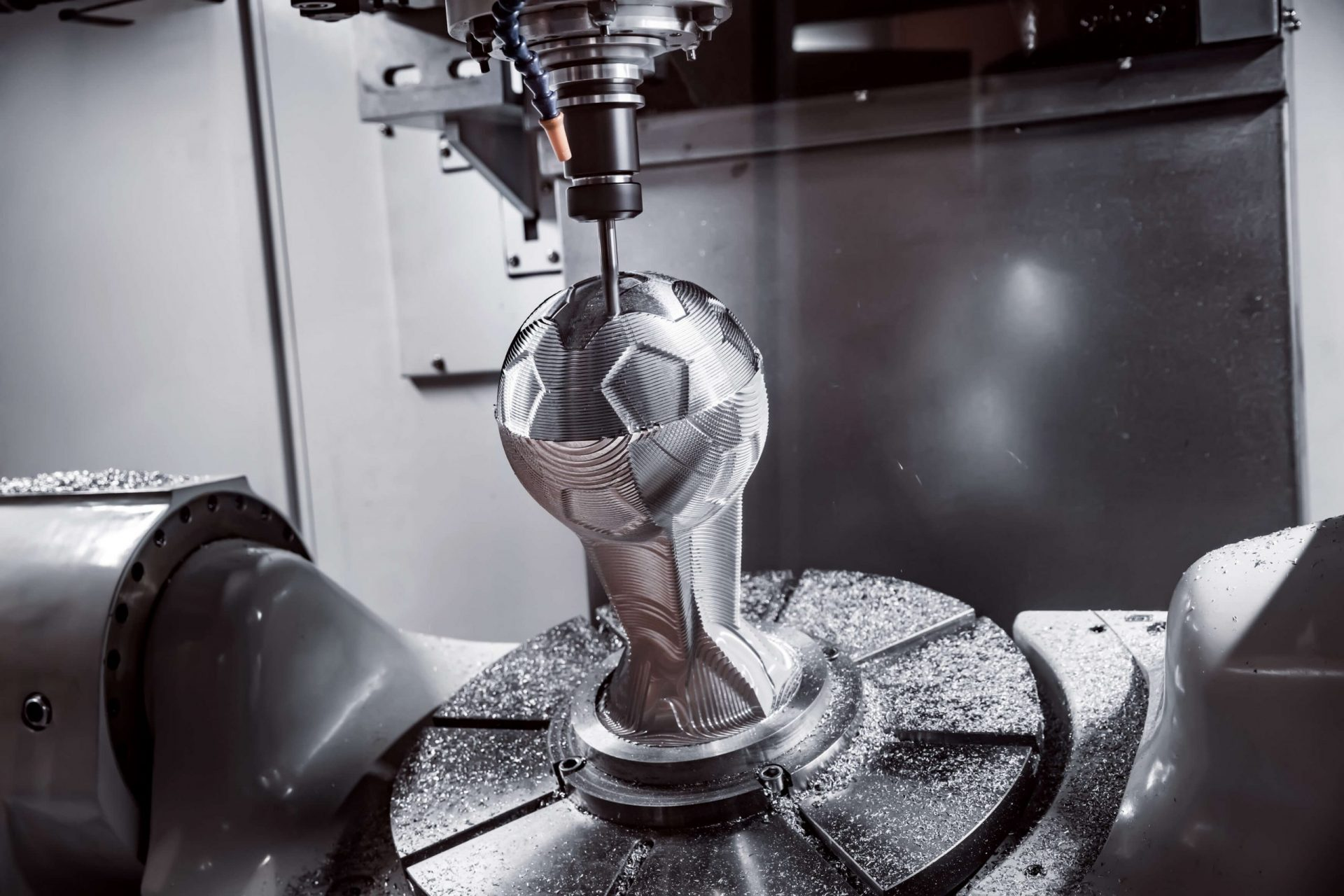

Product Shapes
CNC milling and routing methods often do not give preferred results with round or cylindrical workpiece design. The parts may fall out of measurements in many cases.
Therefore, CNC turning helps get the job done efficiently. As a result, the CNC tuning process is perfect for manufacturing essential parts for different industries. These components include like nuts and bolts, nozzles, rollers, bullets and firearms, barrels, ball jointing, and rounded tables.
Similarities between CNC Milling and Turning
Despite their differences, there are some similarities to keep in mind between CNC turning and CNC milling. These similarities include:
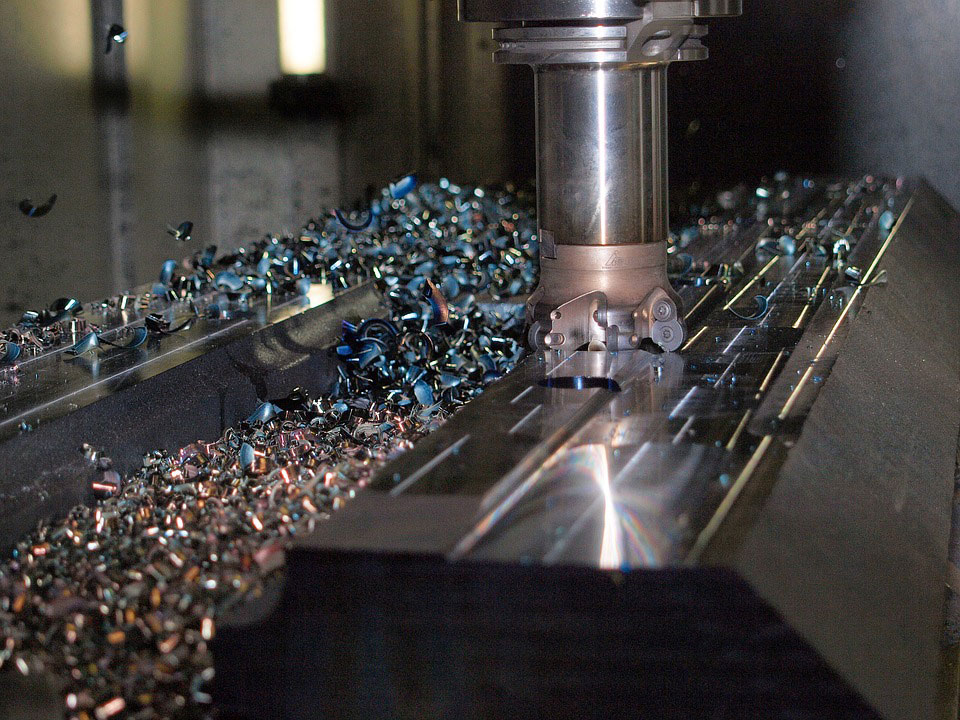

Subtractive Processes of Manufacturing
CNC milling and turning are common processes that follow generally accepted CNC machining principles. Material is extracted from a solid 3D block to achieve a desired part. These two processes use specialized cutting mechanisms to produce parts with the final desired shapes by removing material through grinding, riling, and cutting.
Use of Latest Computer Numerical Control Technology
The milling and turning methods are conventional CNC machining methods. In these process, results are easier and faster than the traditional machining methods. Each project use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to ease the process of manufacturing.
The importance of the CNC file format is to generate a set of code for the milling and turning known as ‘G-code.’ This code is the universal language for CNC Machining. There are hundreds of G-codes that work for both CNC turning and milling.
This means that turning and milling operations require little or no supervision. Since human error is limited, manufacturers can fast-track operation time while maintaining a high quality results.
Similar Cutting Tools
Even though these two processes have different modes of operation, their cutting tools are identical to a certain degree. Both manufacturing processes use solid cutting tools to remove material from parts.
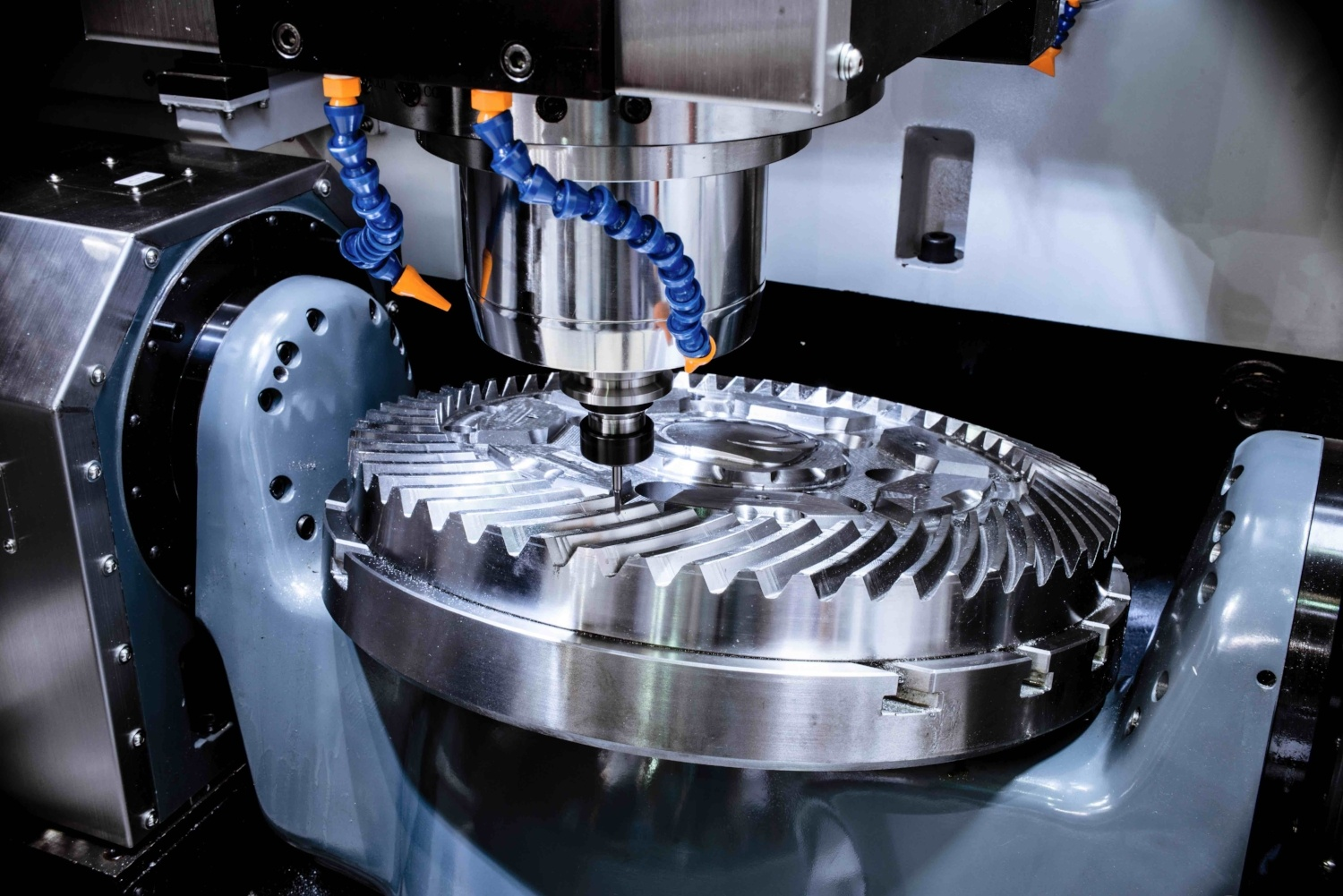

Nonetheless, the configuration and functions of the cutters for both methods differ. Chip formation is a characteristic feature that is common to both processes.
Good Surface Finish
These processes are different, but they have the same aim or result. Both techniques work on workpieces that need cleaning and a finishing touch, and these parts are worked on to produce the best achievable surface finish.
Although, results are dependent on certain factors such as the cutting velocity, depth of cut, feed rate, cutting environment, and tool geometry.
Heat Generation from Cutting Tool
Both CNC milling and CNC turning require cutting fluid to function well. Both processes are bound to produce heat during operations. Also, the operations involved in both processes may be influenced by high cutting temperature.
Differences between CNC Milling and Turning
CNC mills rotate cutting tools on the surface of a still workpiece at high speed. The spindle clasps onto the milling cutter or cutting tool that spins at high speed and cuts away material. Depending on the requirements, a cutting tool in a CNC mill often has 2-150 cutting surfaces or more.
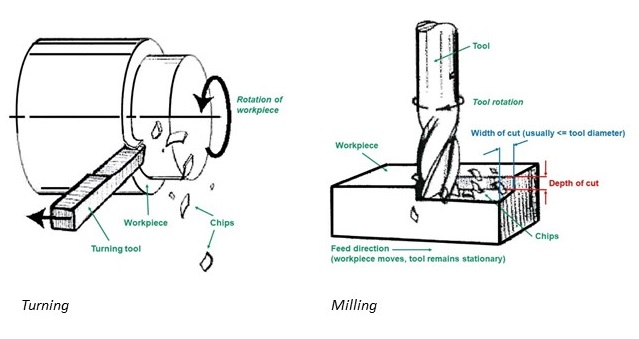
On the other hand, CNC turning machine or CNC lathe has a gripping tool (a chuck) that holds on to the cylindrical bar stock. A spindle spins the gripping tool and material at a programmed speed rate while a stationary cutting tool shaves the surface of the workpiece.. Here, the conical workpiece rotates at a pre-set RPM.
Milling operations are perfect for parts with flat surfaces on rectangular blocks. The cutting tool applies an intermittent cutting throughout the procedure; CNC milling has a multi-point cutting tool (milling cutter).
There is only a single point cutting tool in CNC turning. Several CNC lathes have outer diameter limitations, tooling options, and spindle options.
CNC lathes often create round shapes, but they can also work on many hexagon-shaped bar stocks. Most CNC turning centers have one spindle, which allows them to work on a workpiece from one side. Other turning centers come with the main spindle and a sub-spindle for support. This enables both spindles to work on a workpiece, giving room for additional features if needed.

Basically, the difference between CNC turning and milling machines lies in their mode of operation. Their different operations yield the same results despite their differences.
Bottom Line
CNC milling and turning are two of the most common CNC Machining techniques producing excellent results. However, deciding the most appropriate process for your project depends on your part’s design, tolerances, and geometry.
Cylindrical or conical parts work better with the CNC turning method, while CNC milling is ideal for large, flat, rectangular, or square parts.
Whenever you are unsure of the right process to choose, let AT Machining help you. Contact us today for your CNC machining services, and let’s get you the best results.


